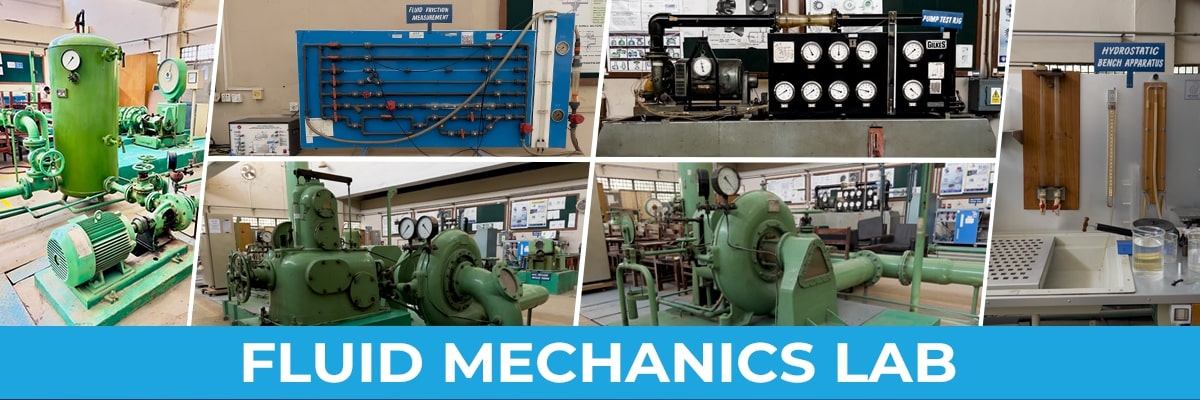
ME-417 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW & PROPULSION SYSTEMS
CREDIT HOURS
Theory = 3
Practical = 0
COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES (CLOs)
| S. No. | CLOs | PLO | Taxonomy |
| 1 | Explain different terms of compressible and isentropic flows | PLO-1 |
Coginitive |
| 2 | Solve cases of different non-isentropic flows such as normal / oblique shock and flows with friction or heat transfer | PLO-2 | Coginitive Level 3* |
| 3 | Analyze various shaft power and aircraft gas turbine engines with their environmental impact | PLO-7 | Coginitive Level 4* |
COURSE CONTENT
- Governing equations for compressible fluid flow: conservation of mass, momentum and energy.
- Sonic velocity and Mach number, difference between incompressible, subsonic and supersonic flow, propagation of sound waves, equations for perfect gases in terms of Mach number, optical methods of investigation.
- Isentropic flow of a perfect gas, limiting conditions (choking), effect of area change on flow properties, flow in convergent and convergent-divergent nozzles, Hugoniot equation, applications of isentropic flow.
- Formation of shock waves, Weak and Strong waves, stationary and moving shock waves, working equations for perfect gases, operating characteristics of converging diverging nozzle, supersonic diffusers and pitot tube.
- Governing equations for oblique shock waves and Prandtl-Meyer flow, Shock Polar, variation of properties across an oblique shock wave, expansion of supersonic flow over successive corners and convex surfaces.
- Fannoline, friction parameter for a constant area duct, limiting conditions, isothermal flow in long ducts.
- Flow in ducts with heating or cooling, thermal choking due to heating, correlation with shocks.
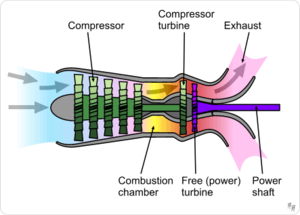
- Propulsion applications including rocket nozzles, rocket engine staging, supersonic inlets, and exhaust nozzles for air breathing propulsion systems. Parametric cycle analysis for ramjet, turbojet, turbofan, and turboprop engines.
- Experimental work on following will be performed in the lab: Use of wind tunnel; determination of Mach Number, drag coefficients of various objects; comparison of aerodynamic designs; pressure distributions on models.
RECOMMENDED BOOKS
(01) Gas Dynamics by M.H. Aksel, O.C. Eralp
(02) Fundamentals of Gas Dynamics by R.D. Zucker & O. Biblarz
*For details of Taxonomy Levels CLICK HERE!